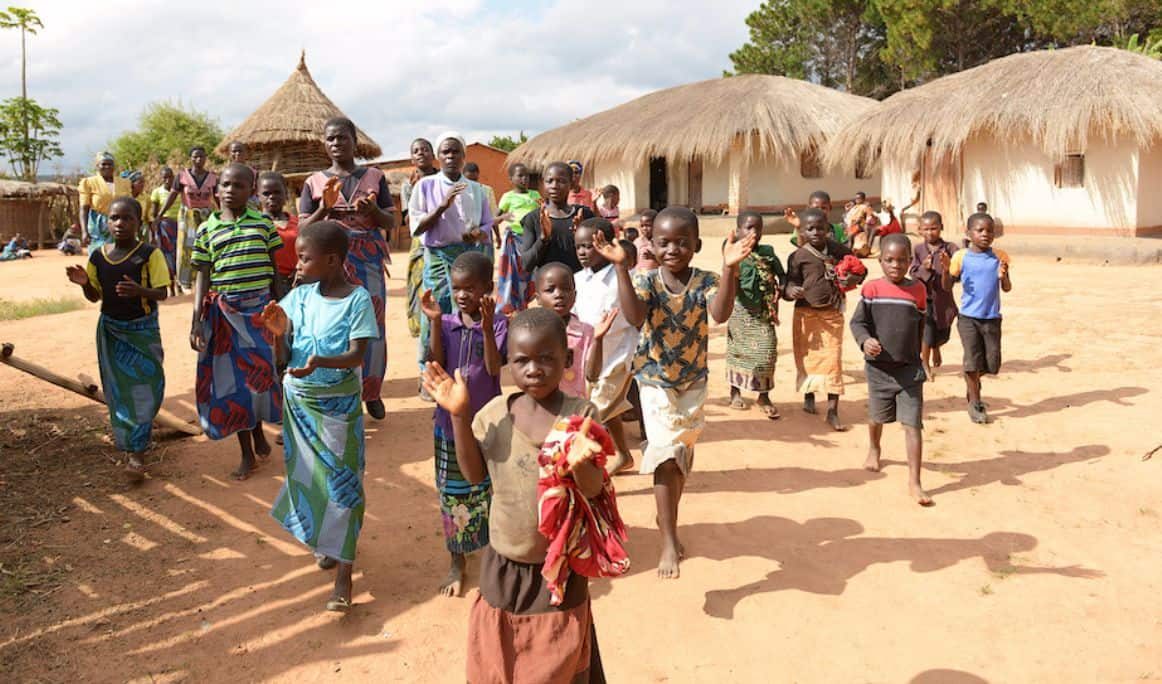
Tourism has emerged as one of the world’s fastest growing industries, serving as a powerful driver of economic development and social transformation. Beyond its contribution to national income, tourism significantly influences employment generation and poverty alleviation, especially in developing economies where other industries may be underdeveloped.
Employment Generation Through Tourism
The tourism sector is labor intensive, creating direct, indirect, and induced employment opportunities. Direct jobs are found in hotels, restaurants, airlines, travel agencies, tour companies, and entertainment services. Indirect employment emerges from supply chains that provide goods and services to tourism-related businesses, such as farmers supplying food to hotels or artisans selling souvenirs. Induced employment occurs when tourism workers spend their income on goods and services, further stimulating the local economy.
In many regions, tourism has become one of the largest employers. According to the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), the sector accounts for about 10% of global employment. For developing countries with rich natural and cultural attractions, tourism provides a platform for diverse job opportunities that often require minimal formal education or training, thus accommodating a wider range of workers.
Tourism as a Tool for Poverty Alleviation
Tourism also contributes directly to poverty reduction by channeling income to local communities. When tourists spend money on local products, handicrafts, food, and cultural experiences, the revenue goes directly into the hands of local entrepreneurs and small scale workers. Community based tourism initiatives where villagers host visitors, organize cultural performances, or manage eco lodges have proven effective in empowering rural populations.
Moreover, tourism can bridge the gap between urban and rural development. Remote communities that traditionally rely on subsistence farming or fishing can diversify their income by engaging in tourism activities. This diversification not only improves household incomes but also reduces vulnerability to economic shocks.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite these benefits, the impact of tourism on employment and poverty alleviation is not automatic. Issues such as seasonality of tourism demand, low wages, lack of decent working conditions, and the risk of economic leakage (when profits are repatriated by foreign owned businesses) limit its effectiveness. Additionally, without careful planning, the benefits of tourism can be unevenly distributed, favoring large corporations over local communities.
Conclusion
Tourism plays a vital role in fostering employment opportunities and reducing poverty, particularly in developing nations with abundant natural and cultural resources. For its potential to be fully realized, governments and stakeholders must prioritize inclusive tourism policies, invest in skill development, and encourage community based tourism. By doing so, tourism can serve as a sustainable pathway toward economic growth and social equity.